External Respiration Is Best Described as
The components of external respiration include alveolar surface area ventilation and perfusion matching and partial pressure gradients. Exchange of gases between the external environment and a distributing system of the animal body as the lungs of higher vertebrates or the tracheal tubes of insects or between the alveoli of the lungs.
Partial pressure gradients allow gasses to flow from areas of high pressure to areas of lower pressure.
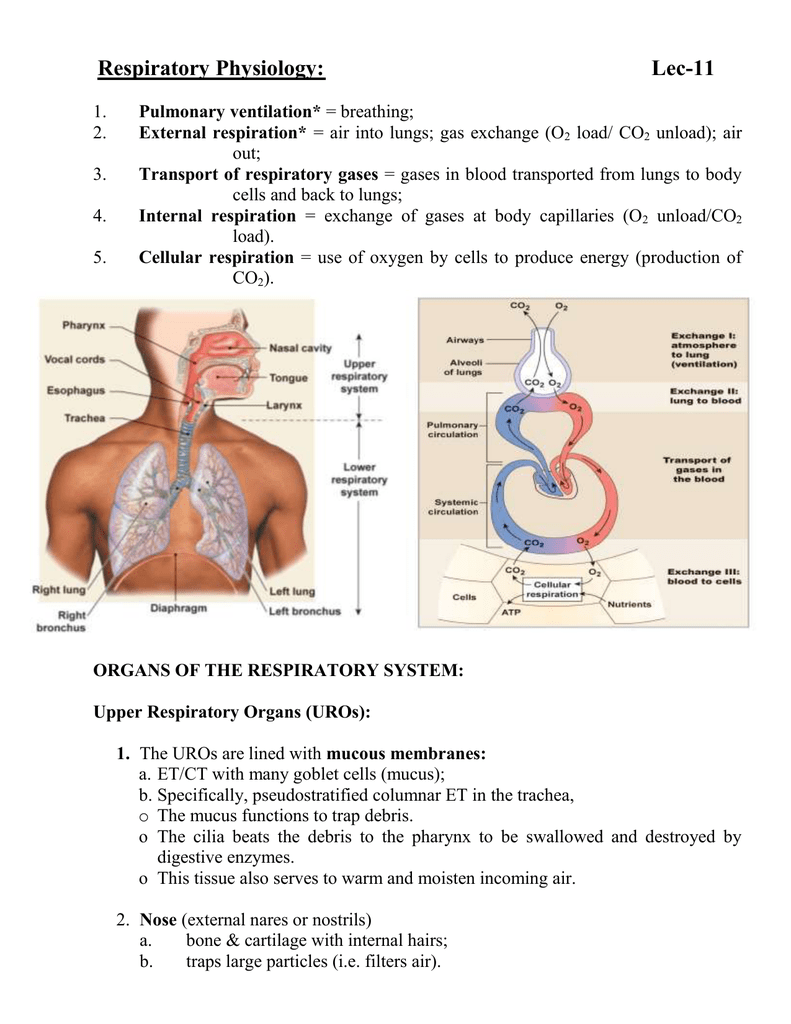
. The first stage involves ventilation or breathing which is the intake of oxygen into the body and expulsion of carbon dioxide out of the body. Oxygen is transported in the blood by binding to. CPartial pressure of oxygen is higher D.
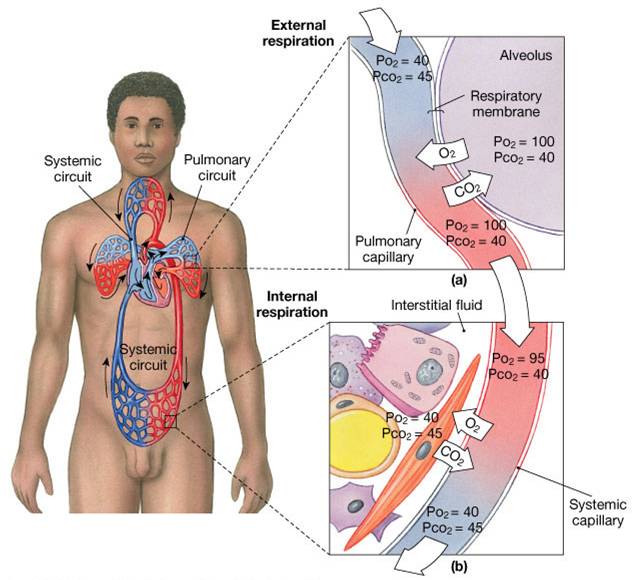
And external respiration The prime function of. Oxygen diffuses from alveolar air into the blood during external respiration. Which of the following accurately describes the site of external respiration.
It is an exchange of gasses between the blood and the individual cells of the body. External respiration is best described as the. Chapter 6 Oxygenation and External Respiration Oxygenation These two systems cooperate respiratory and cardiovascular to supply the needs of the tissues.
It allows easy diffusion of gases between the alveoli and the body. Stay tuned with BYJUS to learn more in detail about the respiration process mechanism of breathing mechanism of. The exchange of gases at a cellular level within the body.
Ventilation and perfusion in the. Both A and B. External respiration describes the exchange of gasses between the external environment and the bloodstream.
In what area of the lungs does respiration occur. External respiration is about the mechanics of breathing getting oxygen into the lungs and regulating it in a way that ensures its diffusion into the blood. External respiration is best described as the internal respiration.
Breathing mechanics include breathing rate breathing depth. The process of gas exchange that occurs between the cells and the systemic capillaries is known as. APartial pressure of oxygen is lower in the capillaries than the tissue.
External respiration refers to the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs gills or other tissues exposed to the external environment. It is an exchange of gasses between the air in the lungs and the blood. The active process of inhalation.
The process of external respiration includes the breathing process ie both inhaling intake of oxygen and exhaling outlet of carbon dioxide. It is very thick and covered with a thin layer of mucous. External respiration consists of two stages.
This energy can then be used to produce heat for. Internal respiration refers to the gaseous exchange between blood and different tissues and cellular respiration process where oxygen is utilised to generate energy in the form of ATPs. Oxygen diffuses out from the blood into tissue during internal respiration.
It is also about ensuring proper diffusion of CO2 from the blood into the lungs and its subsequent excretion into the atmosphere. The other supplies blood. Medical Definition of external respiration.
One system supplies air. From prokaryotic bacteria and archaeans to eukaryotic protists fungi plants and animals all living organisms undergo respirationRespiration may refer to any of the three elements of the process. Their ultimate purpose is the transfer of gases between air and all tissue cells.
External respiration refers to the gas exchange across the respiratory membrane of lungs. The external respiration definition is the gas exchange that occurs between the lungs and the environment hence the term external. The passive process of exhalation.
This process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as well as a number of. First respiration may refer to external respiration or the. External respiration refers to breathing and exchange of gases between the external environment and lungs and between alveoli surface and the blood stream.
Up to 20 cash back Which of the following describes external respiration. Respiration is a series of exothermic reactions that occur in the mitochondria of living cells in order to release energy from food molecules. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide is higher in the capillaries than the tissue.
Exchange of gases between the peripheral tissues and the external environment. All of the above describe external respiration. Exchange of gases both in and out of the blood occurs simultaneously.
Exchange of gases between the bloodstream and tissue cells via the surrounding extracellular fluid. The exchange of gases at alveoli level within the lungs. External respiration is the process of exchanging oxygen carbon dioxide and other blood solutes with the external environment.
Breathing is the mechanical process of pulling lungs into or out of the lungs or moving water over the gills. It is composed of tissue cell membranes a thin layer of connective tissue and the wall of a systemic capillary. External respiration is a physical process of taking oxygen from the external environment into the body and expelling carbon dioxide from the body to the external environment.
External respiration also known as breathing refers to a process of inhaling oxygen from the air into the lungs and expelling carbon dioxide from the lungs to the air. It is an interaction between the diaphragm and the abdominal wall causing the air to move into and out of the lungs. It is a vital process for life as it supplies oxygen to extract energy from food via internal or cellular respiration.
External respiration describes respiration that occurs between the external environment and the cells of the body. Respiration in whole is the process of delivering oxygen to the cells to extract the energy from sugars in oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Respiration is the process in which organisms exchange gases between their body cells and the environment.
External respiration can be described as. It is the trachea bronchi and bronchioles. The exchange of gases as oxygen and carbon dioxide between the cells of the body and the blood by way of the fluid bathing the cells compare external respiration WORD OF THE DAY.
Which of the following best describes external respiration. Exchange of gases between the alveoli and the external environment through breathing.
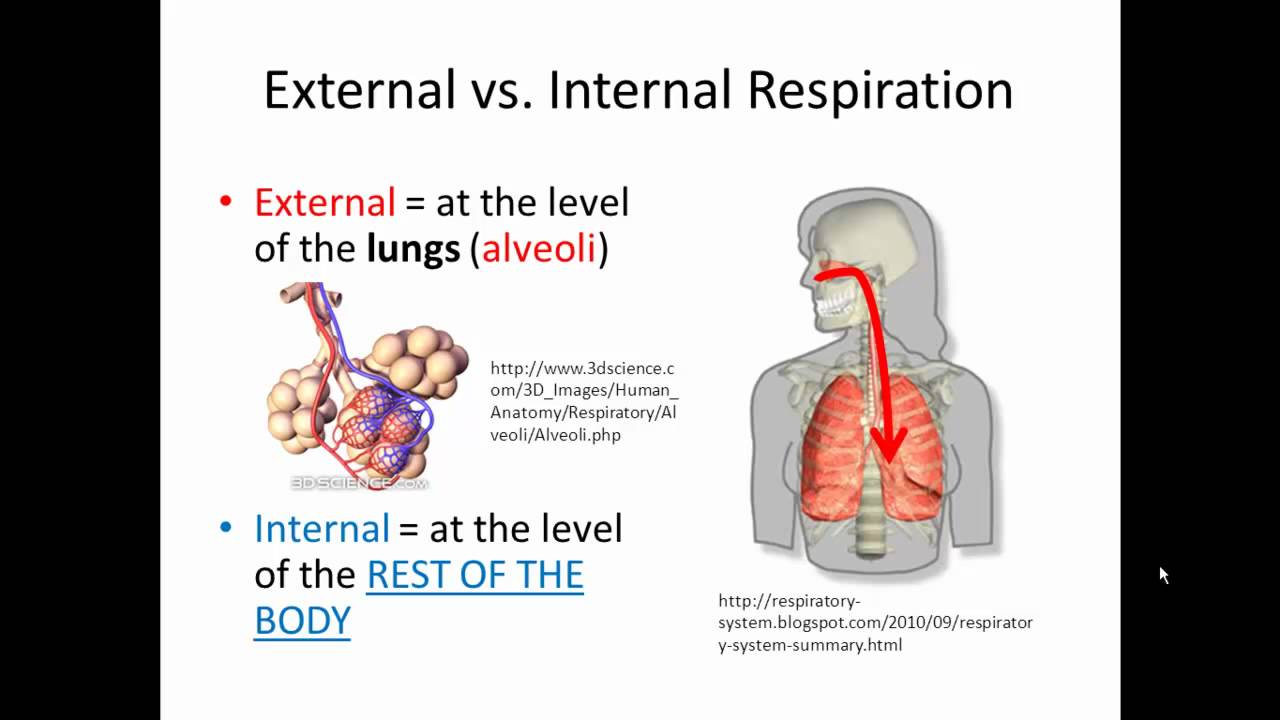
External And Internal Respiration Gas Exchange Simplified Youtube
No comments for "External Respiration Is Best Described as"
Post a Comment